S/MIME vs. OpenPGP | What’s the difference?

Sending secure emails is an important part of successful communication in business. Find out which of the two encryption standards, S/MIME or OpenPGP, is a better fit for your security requirements.
Published by

Carina Prüll
Date
With approximately 347 billion emails sent and received worldwide every day, it is important to understand the role encryption plays in protecting sensitive data to minimise the risk of cyber incidents and abuse. The choice between S/MIME and OpenPGP for encrypting emails can have a significant impact on the security and efficiency of your business communications.
The implementation and use of encryption systems, especially asymmetric encryption methods, enables companies to protect their most valuable resource – their own data – from unauthorised access. Companies need strong encryption systems that users can trust. After all, email is still the number one means of communication and it is impossible to imagine today’s digital landscape without it.
In this article, we take a closer look at the differences between S/MIME and OpenPGP. We explore the question of which of the two encryption methods offers the most comprehensive support for your business communication and therefore fulfils the specific requirements of effective and user-friendly email security for business partners and colleagues.
S/MIME vs. OpenPGP – Why is this decision so important?
S/MIME and OpenPGP are two different encryption technologies that can be applied to emails. Both standards can be integrated into common email programmes with a little effort, offering a gain in security that makes for convenient handling of encryption for text-based communication.
“Encryption works. Properly implemented and strong encryption systems are one of the few things you can rely on.” – Edward Snowden, US whistleblower
Companies need functioning and robust email encryption systems. S/MIME (Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions) and OpenPGP (Open Pretty Good Privacy) offer two solutions that are used for the purposes of digital trust and email security. However, it is important to realise that the two encryption methods are not compatible with each other. Both technologies take different approaches to email encryption and offer different advantages and disadvantages. One of the most common reasons why the choice between S/MIME and OpenPGP is relevant for companies is reflected in the somewhat costly implementation.
The decision between S/MIME and OpenPGP depends on various specific requirements, the existing infrastructure and the preferences of a company. But one thing is certain: with S/MIME, numerous companies are opting for the world’s leading email security standard – and not just in the business environment. Digital signatures from certified CAs ensure that emails are optimally secured and smooth email communication is guaranteed.
S/MIME – the basic principle and how it works
S/MIME is a standard for the secure transfer of emails. Specifically, it is a common encryption and signature method that is primarily used for emails to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of messages. Like OpenPGP, it has been around since the 1990s and is constantly evolving.
Emails can be digitally signed and encrypted with S/MIME. The digital signature enables the recipient to verify that the message actually originates from the specified sender and has not been altered during transmission. Consequently, S/MIME protects the content of the message from unauthorised access by making it readable only for authorised recipients.
S/MIME also uses certificates issued by certification authorities (CAs) such as DigiCert to verify the identity of the sender and generate the encryption keys. These certificates are usually integrated into email clients like Microsoft Outlook or Mozilla Thunderbird. The aim is to enable the seamless integration and utilisation of the S/MIME functionality.
Email security with S/MIME
- S/MIME protects your emails from being read, stored, manipulated or deleted by third parties.
- Data protection-compliant security measures ensure the secure and standardised transmission of sensitive information.
- Data sovereignty is increased by authenticating the sender and content of emails.
- S/MIME can be used as the standard for all email traffic and can be configured manually as required.
6 Determining factors for the use of S/MIME
The decision to use S/MIME certificates is based on certain factors that play a relevant role, especially with regard to implementation. In addition, there are internal compliance guidelines, strategic decisions on security dimensions and other measures for setting up, maintaining and properly managing certificates that require GDPR-compliant emails.
We have compiled 6 important determining factors for the use of S/MIME, which go far beyond the standard security requirements of an organisation.
1 Sensitivity of information
The degree of sensitivity of the information being transmitted influences the likelihood of using S/MIME certificates. Particularly in healthcare, financial services or legal sectors, S/MIME can be of decisive significance when exchanging confidential information.
2 Government regulations and internal policies
Many industries in which privacy and security are particularly important tend to use S/MIME. The use of S/MIME may even be required or recommended by industry standards or government regulations. Internal company policies can also influence the use of S/MIME to ensure the integrity, authenticity and confidentiality of messages and sensitive data.
3 Certificate management
S/MIME certificates for secure e-mail communication and TLS/SSL certificates for authenticating network connections fall into the category of digital certificates. It describes a centralised trust model of the public key infrastructure (PKI). The availability and management of these certificates can be decisive when choosing between S/MIME and OpenPGP.
DigiCert is the world’s leading provider of TLS/SSL, S/MIME, code & document signing certificates. As a proud Premium Elite Partner of DigiCert, we fulfil the highest security standards to effectively protect your online communication.
4 Cost effort
Nevertheless, it should be noted that the associated costs also play a role. The costs of implementing and managing S/MIME may include the purchase of additional certificates, training for users and administrators and any software or infrastructure updates.
5 Compatibility
For example, if an organisation uses different email clients, it is important to ensure that S/MIME can be seamlessly integrated. The compatibility of S/MIME with different email clients and platforms can therefore have a huge impact on the decision.
6 Usability
Basically, it should be noted that the implementation of S/MIME is simple and transparent. The usability of S/MIME-enabled email clients and services can ultimately have a significant influence on acceptance.
Advantages of S/MIME
What are the advantages of using S/MIME? We explain how effective S/MIME certificates are for encrypting and digitally signing emails in business.
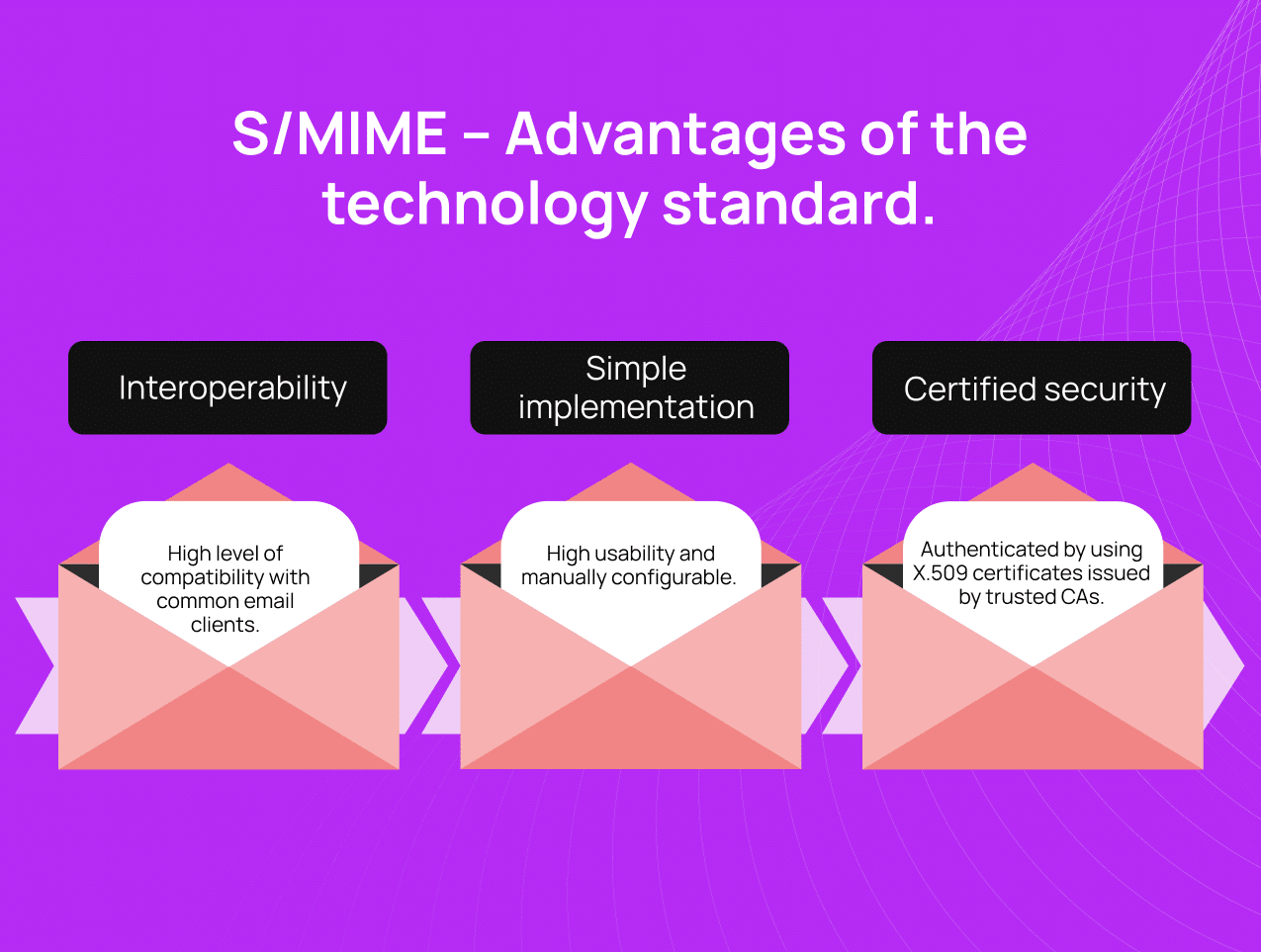
Interoperability
S/MIME is supported by almost all common email clients and servers and therefore has a high level of application security and interoperability – even between the email clients of providers with the highest market shares such as Microsoft Outlook, Windows Mail, Mozilla Thunderbird and Apple Mail. In most cases, it requires no additional software installations or configurations.
Simple implementation
S/MIME often integrates better into business environments, especially when organisations use Microsoft products such as Outlook. Although certificate management can be a challenge, seamless integration into enterprise platforms is achieved, which is why the option of manually setting up S/MIME is an advantage over OpenPGP. In addition, mail gateways give admins more scope for company-specific configurations.
Certification authorities provide security
S/MIME uses X.509 certificates, which are issued by a certificate authority (CA). They enable higher levels of trust.
CAs ensure that keys and owners really belong together and provide certainty. This form is not available with OpenPGP.
S/MIME classifications by CAs
- Class 1: Check to verify whether the specified email address exists.
- Class 2: In addition to the email address, the name and, if applicable, the company are confirmed in writing.
- Class 3: The user of the certificate must authenticate their identity by submitting personal identification
- Class 4: The certificate owner proves their identity by appearing in person at the relevant certificate authority.
InterNetX works with all leading CAs. Discover our S/MIME products and classify your email business to the highest standard.
Challenges and limitations of S/MIME
S/MIME offers many advantages, but the use of certificates can also have limitations.
Size restriction for file attachments
Although some S/MIME solutions have additional modules for transferring large file attachments, this is usually associated with an additional charge.
No compatibility with OpenPGP environments
Alongside OpenPGP, S/MIME is one of the most frequently used solutions for email encryption and is highly compatible with various email clients and application systems. However, if a recipient uses S/MIME and a sender uses OpenPGP, they cannot exchange key pairs as the two different methods are not compatible with each other. It also requires users to perform a manual backup on the recipient side to overcome this hurdle.
Use and immutability of static keys
S/MIME solutions use static key pairs according to the asymmetric principle:
- Encryption → public key
- Decryption → private key.
These remain unchanged for all correspondence during their entire period of validity. If third parties have unauthorised access to the communication and a private key is compromised, not only can an email from the person concerned be viewed, but all data that can be decrypted with the compromised key can also be viewed retrospectively.
Unencrypted metadata
While messages are protected by encryption during transmission, other metadata, such as the subject line, remain unencrypted.
Costs
The permanent implementation of S/MIME can be costly, as commercial certificates must be purchased from a trusted CA. So the investment may ultimately prove to be worthwhile.
The security of email communication in business is a top priority. This makes it all the more important to understand these restrictions and challenges and to take them into account when making decisions about the use of S/MIME. Our experts at InterNetX will be happy to advise you honestly and without obligation.
Increase trust with business partners and customers. Ensure greater transparency in email communication with S/MIME certificates and effectively protect your business against phishing and spoofing.
OpenPGP – the basic principle and how it works
OpenPGP is another method in the field of email encryption. Open PGP stands for “Open Pretty Good Privacy” and is an open standard for the encryption and digital signature of data, including emails, files and directories.
With OpenPGP, users can create digital signatures to verify the authenticity of data. The recipient can ensure that the data actually originates from the specified sender and that it has not been altered during transmission.
Key exchange is the basic requirement for encrypted email communication using OpenPGP. This means that your own public key must be known to the desired communication partner – either by direct transmission or by uploading it to an external key server. This requires the implementation of a few intermediate steps and the additional verification of the key’s authenticity.
8 determining factors for using OpenPGP
If you want to use OpenPGP for your email encryption, you need to lay the appropriate foundation beforehand. Here are 8 determining factors for deciding in favour of using OpenPGP:
1 Technical knowledge
Solid technical knowledge is required to even correctly determine which specific OpenPGP solution is required for your IT requirements. The implementation of OpenPGP requires considerable effort.
2 High willingness
Contact partners must also be willing to go to any effort and expense to ensure that their own efforts are not in vain. Anyone who relies on OpenPGP as a solution for email traffic must therefore also ensure that external contacts manage to do so successfully.
3 Free availability
The free availability of open source implementations such as GnuPG makes OpenPGP particularly attractive for companies looking for a cost-effective solution.
4 Flexible key management
OpenPGP offers mechanisms for managing public and private keys and can be used on various operating systems and platforms. This can be a particularly suitable solution for companies that require flexible key management.
5 Users anonymity
OpenPGP is also useful if users value anonymity and want to send messages without a direct link to their identity.
6 Cost and manual effort
When setting up OpenPGP manually, it is important to bear in mind that it often leads to further costs.The purchase of additional software is required to avoid potential security risks.
7 Compliance
The complex implementation of OpenPGP increases user errors and risks for data protection and compliance. For user-friendliness, it requires a great deal of time and money (installation, training). In industries with strict security standards, this can promote compliance requirements.
8 Integrity
OpenPGP is not only suitable for email encryption. It can also be used for encrypting files and directories. As with S/MIME, digital signatures are required to verify the integrity and authenticity of the data, especially in relation to emails or files.
Remember: For the vast majority of users, OpenPGP remains a technical solution with many requirements for users. At the same time, the technology prevents mass suitability, because the key management is complex and is usually only employed by and among IT-savvy users – mostly in private spheres.
Advantages of OpenPGP
The effective use of OpenPGP can demand a certain learning curve, especially with regard to handling and managing keys. However, the open source standard also has its advantages.
Openness and transparency
OpenPGP uses a decentralised approach, the so-called “web of trust”, to verify key authenticity. This is based on the mutual trust of all parties involved. It is a manual process without a centralised authority.
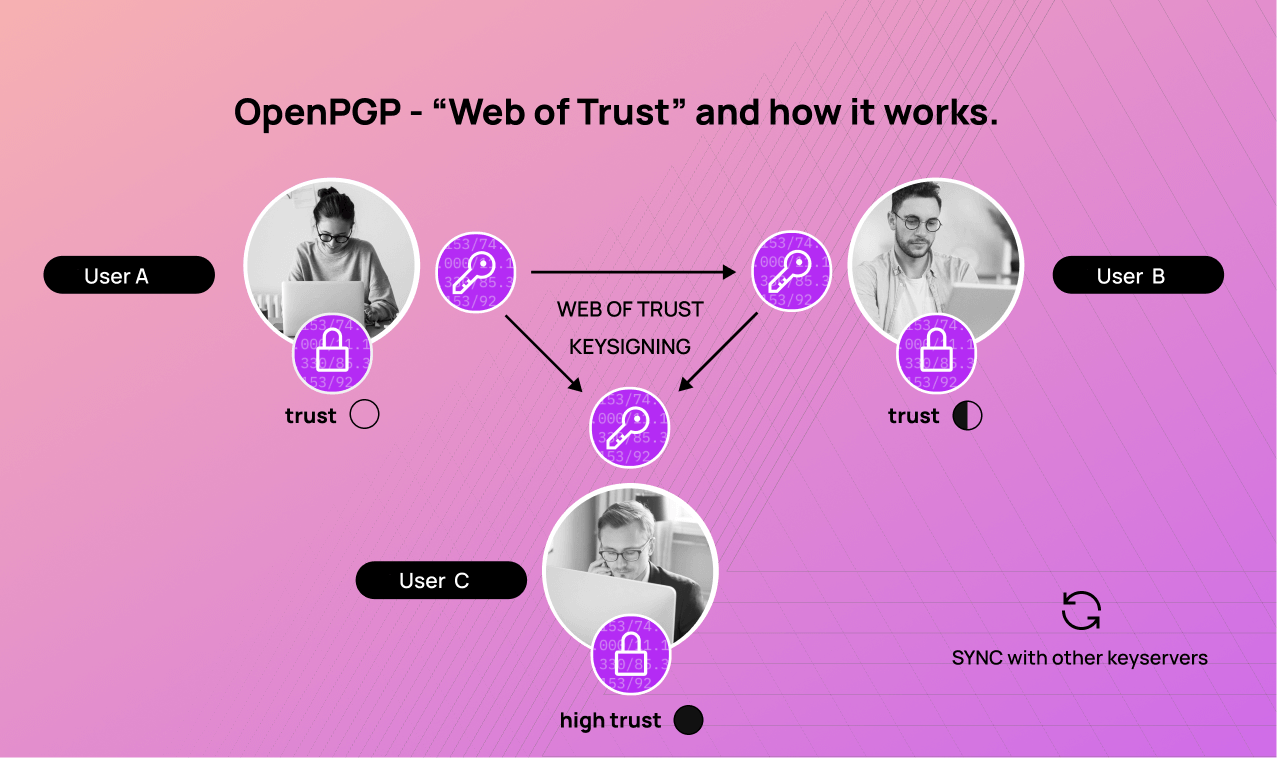
The more users, the higher the degree of credibility for the key categorised as trustworthy. A certificate is created with each new signature, which increases security. In contrast to S/MIME, however, there is no clear verification of digital signatures by audited CAs.
The OpenPGP standard is supported by a large number of applications and platforms, including email clients such as Mozilla Thunderbird and GnuPG (GNU Privacy Guard).
Open source
Users who use webmail services can also use OpenPGP for email encryption. Appropriate browser extensions can be used to apply common methods such as JavaScript implementations of the OpenPGP standard for multiple browser versions.
Online PGP tools offer the option of generating keys and encrypting and decrypting emails. For this purpose, there are a number of free open source services which do not require registration and can be run in browsers without any problems – albeit at an additional cost.
OpenPGP is also supported by a dedicated community of developers and users. They contribute to the continuous development and improvement of OpenPGP technology.
Web of Trust
The “Web of Trust” creates a high level of trust by actually matching the generated and certified key with its specified owner. It enables the strong encryption of data, including emails, files and directories, and protects it against unauthorised access. OpenPGP helps to maintain anonymity by allowing messages to be sent without a direct link to the sender’s identity.
The ability to create digital signatures also enables OpenPGP to verify the integrity and authenticity of data. When signing, a unique fingerprint is generated from the plain text of the respective message using a cryptological hash function (SHA-256), which is encrypted with the sender’s private key and attached to the message.
This combination of advantages makes OpenPGP a good option for those looking for an open and platform-independent solution for secure communication. However, caution is also advised. When it comes to sensitive, business-critical and internal information, S/MIME is a more powerful option – especially when it comes to the highly secure and standard-compliant transmission of content. The provision of digital certificates from certified CAs guarantees the best functionality and security.
Challenges and limitations of OpenPGP
There are various basic problems with OpenPGP solutions that may present a particular challenge for companies.
Complexity
Setting up OpenPGP can be complex for less experienced users without sufficient IT knowledge and thus create disadvantages for the broad acceptance of OpenPGP. In addition, the use of OpenPGP on mobile devices is quite difficult. There is no approach that is equally suitable for all end devices or operating systems.
Interoperability
The signatures of keys by other people contain a list of all those who have checked it and confirmed the identity of the key owner. In terms of data protection, this is an aspect that users should be aware of.
Data sovereignty
Restrictions on data sovereignty must also be considered. As key servers synchronise globally with each other, uploaded keys can be accessed quickly and from anywhere. Compared to S/MIME, OpenPGP may not be as seamlessly integrated into standard email clients. This could affect overall usability and hinder adoption.
In addition,OpenPGP is not as widely used as other security solutions in many organisations. Both inside and outside of corporate networks, this could limit the ability to communicate securely. This also includes the aspect that all contacts who do not use software for OpenPGP encryption are left out.
Loss of metadata
Another disadvantage is the potential loss of metadata. As the email header remains encrypted, metadata such as the sender, recipient and subject line can still be viewed by third parties.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of OpenPGP is often determined by the specific implementation and the willingness of users to deal with the key management aspects. In this respect, a centralised trust model can be easier to manage and monitor in corporate and business environments.
With the X.509 certificate, S/MIME uses a strictly hierarchical system for the certification of public keys. A certification authority (CA) is always at the top of the certification hierarchy and signs the keys of all participants within the public key infrastructure (PKI) either directly or via its sub-authorities. The individual users are in possession of their own key and the public CA key and can therefore check the validity of unknown certificates without restriction and with the highest level of trustworthiness.
In many ways, this scenario promotes a standardised and coherent security line for validating the identity of a communication partner.
Utilise the power of S/MIME – more standards, more trust
The use of S/MIME for encrypting the content of data transmitted by email remains the undisputed ultimate email security solution. The technology has established itself as the global standard for email encryption as it offers effective protection and is based on recognised standards.
Technical details of the current S/MIME version 4.0, as specified in RFC 8551, show further development in terms of cryptographic algorithms and security protocols. In particular, improvements have been implemented with regard to the length of keys and the supported encryption algorithms in order to fulfil current security requirements.
The seamless integration of S/MIME with the public key server “Open Keys” not only provides additional security, but also enables particularly easy implementation. Open Keys acts as a central hub for the provision of public keys and only checks trustworthy trust centres. This mechanism ensures that only authenticated keys are used, which in turn strengthens trust in encryption communication.
Technically savvy users benefit from the openness of the Open Keys system as it promotes the interoperability of S/MIME encryption across different platforms. Compared to proprietary solutions, Open Keys offers a considerable advantage by enabling S/MIME-based encryption not only within provider-specific appliances. Standardised communication via common protocols plays a decisive role here, facilitating integration into existing infrastructures.
In addition to the basics of S/MIME and Open Keys, technical insights into protocol mechanisms and encryption methods open up a deeper level of understanding for security experts and IT professionals.
In business matters, we rely on the highest level of trustworthiness. Our InterNetXperts will advise you on all our high-end products in the areas of domains, hosting and encryption. Get your S/MIME certificate, issued by leading CAs worldwide, and quickly find the right certificate for each of your projects on our all-in-one AutoDNS platform.