Digital trust | The bedrock of business success
Digital trust is no longer a luxury, but a vital component of a successful business strategy.
Published by

Simone Catania
Date
In today’s rapidly evolving digital landscape, the need for secure interactions between businesses, customers and stakeholders has never been more critical. As more and more aspects of our lives are transitioning to online spaces, the importance of fostering digital trust – the confidence that digital ecosystems are secure and reliable – is increasingly taking center stage.
Undoubtedly, the future of online business depends on digital trust. Maintaining this level of trustworthiness helps companies stay competitive and provide a robust, secure foundation for enhancing customer relationships. Join us as we navigate the complexities of digital trust and explore its significance for the business world.
What is digital trust?
Digital trust is the backbone of the modern digital landscape, operating in the undercurrents of our business and personal online interactions. At its core, digital trust refers to user confidence in a system, platform or digital environment to protect and maintain their data and digital transactions. It depicts the technical aspects of cybersecurity and data protection and includes the ethical handling, management and use of data.
In today’s business sphere, the importance of digital trust has grown exponentially – so much so that many consumers have declared that they would consider switching brands when a company’s data practices are unclear.
Digital trust is the confidence consumers place in a company’s digital presence, whether websites, applications or digital services.
Without trust, customers are reluctant to share personal data or conduct transactions and consequently, business success can be compromised. For this reason, digital trust is the cornerstone of a thriving digital economy and a non-negotiable asset for any forward-thinking business.
Businesses are responsible for secure digital interactions
The emergence of digital platforms as key channels for commerce and communication has necessitated a heightened emphasis on digital security. As we navigate the digital landscape, the threat of cybercrimes remains high. Today’s businesses, small and large, have the crucial responsibility of protecting their own and their customer’s sensitive data. To that effect, implementing a robust security framework, continuing cybersecurity updates and investing in employee education and awareness are no longer just options for businesses; they are exigent priorities.
The dynamic bond between digital trust and cybersecurity
The foundations of digital trust lie in robust cybersecurity measures, the transparency of data protection protocols and the authenticity of digital identities. Breaches in data can lead to a massive loss in consumer confidence and potentially ruin a brand’s reputation. Therefore, businesses must pay significant attention to securing their digital operations and make appropriate investments in IT security and safety measures.
Therefore, cybersecurity essentially feeds into and lays the foundation for digital trust. The two concepts work together harmoniously, creating a virtuous cycle where stronger cybersecurity fosters increased digital trust, stimulating the demand for even higher levels of security in the digitized landscape. This symbiotic relationship is integral to building a resilient and resourceful digital environment.
Digital trust: Key trends and insights
- Surge in digital transactions: E-commerce sales hit an estimated $5.8 trillion globally in 2023. And total global e-commerce sales are projected to grow by 50% over the next three years, highlighting an increased need for trust in digital platforms.
- Increased data breaches: 2023 recorded an alarming increase in total records exposed in breaches the past year. Over 110M accounts were leaked in the second quarter of 2023 — 2.6 times the number of breaches in the year’s first quarter (43.2M). The global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was USD 4.45 million, a 15% increase over three years.
- Regulatory focus: The implementation of, amongst other, GDPR and the NIS2 Directive in the EU and CCPA in California represent a global trend toward compliance regulations for digital trust.
Building secure cyber networks: four pillars of digital trust
This foundation of digital trust is anchored by four critical components: established standards, diligent compliance and operations, rigorous public and private certificate lifecycle management, and consistent delivery across all ecosystems. Now, let’s delve deeper into each component’s detailed description and analysis.
-> Standards are established by authoritative technology and industry leaders, mirroring the role of the CA/Browser Forum in defining standards for digital certificates. This leads to a universal criterion for digital trust.
-> Compliance and operations refer to the enforcement of policies and the execution of audits. This ensures that all practices are in line with established standards. These operations, principally rooted in data centers, authenticate certificates’ status using protocols like the Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP).
-> The public and private certificate lifecycle management involves software that grants centralized visibility and control over digital certificate lifecycles. It ensures control and trust within an organization, whether public or private.
-> Finally, delivery across all ecosystems pertains to the propagation of trust into intricate supply chains, device lifecycles and the digital rights provenance of content communities. This entails extending trust beyond organizational limits and solidifying the entire e-space as a trustworthy entity.
Together, these components reinforce the structure of digital trust in an increasingly interconnected cyberspace.
The role of PKI in establishing digital trust
The bedrock of digital trust in the business environment often involves the implementation of robust security structures such as the public key infrastructure (PKI). The PKI is a set of hardware, software, policies, procedures and roles that yield secure digital certificates for organizations. These digital certificates play a prominent role in ensuring that digital entities can establish, maintain and prove their identities.
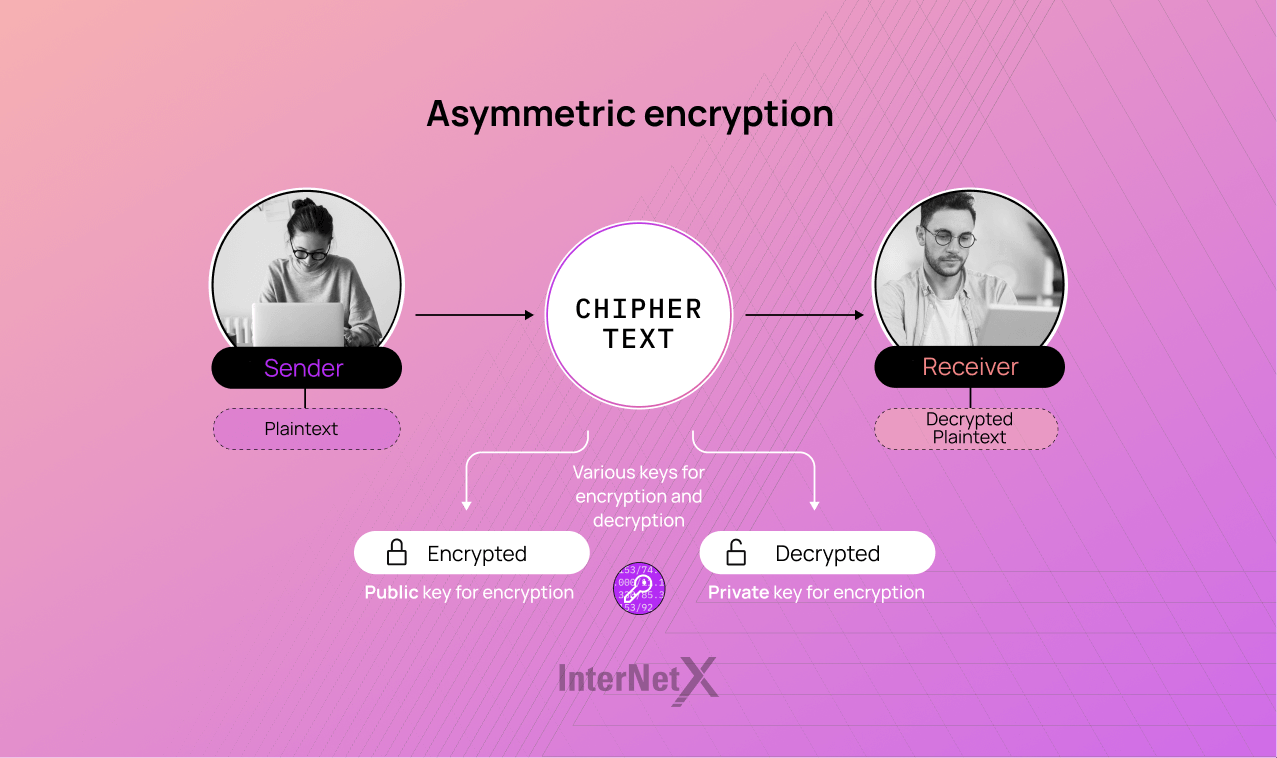
The core concept underpinning PKI is asymmetric cryptography, which involves two keys (public and private keys) to secure digital communication or transactions. The public key, accessible to everyone, encrypts information, whereas the private key, only known to the recipient, decrypts it.
In essence, PKI allows for secure data transmission over the internet and verifies the credentials of any parties involved. By fostering trust and enhancing security in digital ecosystems, this infrastructure proves indispensable to businesses engaged in online transactions or those looking to protect sensitive customer data.
Addressing the constantly evolving world of cybersecurity threats, PKI ensures that identities are verified and that data remains secure—one of the primary aspects of maintaining digital trust!
The role of PKI in enhancing digital trust underscores the importance of responsible digital certificate issuance and management.
The core of digital trust: encryption, identity and integrity
As the threat of data breaches and cyber attacks is growing, businesses are forced to prioritize building and maintaining digital trust. Organizations must focus on three core elements to accomplish this, namely encryption, identity and integrity.
-> Encryption: protecting data in transit and at rest
The role of encryption in safeguarding data and trust cannot be overstated. Encryption is the process of encoding sensitive information that can only be accessed and read by the authorized parties possessing the required decryption key. Whether data is in transit (moving across the network) or at rest (stored on servers or storage devices), encryption is crucial in protecting valuable information from unauthorized access, making it unintelligible to any unauthorized party.
Take, for instance, the Transport Layer Security (TLS), Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Secure/Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions (S/MIME) used in various web platforms. These technologies serve to secure communication online. While TLS and SSL encrypt the data transmitted between a user’s browser and the web server to prevent unauthorized parties from intercepting or tampering with it, S/MIME plays an essential role in encrypting and decrypting email messages in MIME format to ensure that they remain confidential and verified during transfer.
-> Identity: implementing strong identity controls
Identity management is essential in establishing digital trust by limiting access to sensitive information to the right individuals or systems. By implementing robust identity management measures (user authentication and authorization), companies can restrict unauthorized access to critical data and resources, lowering the risk of data manipulation or theft.
One way to implement identity management is through the use of multi-factor authentication (MFA) or two-factor authentication (2FA), for which users must provide at least two pieces of evidence (usually a password and a temporary code sent to a mobile device) to verify their identity. Another valuable asset in identity management is document signing certificates, which add a layer of security by confirming and securing the signatory’s identity, ensuring the document’s authenticity and integrity.
Additionally, some companies adopt single sign-on (SSO) solutions, allowing users to access multiple applications with a single login credentials. SSO streamlines the overall user experience and reduces the number of passwords to be managed and associated security risks.
-> Data integrity: safeguarding consistency and accuracy of information
Data integrity is crucial for establishing digital trust and protecting users’ data, ensuring a secure and reliable online environment. As the foundation of digital trust, data integrity focuses on maintaining the accuracy and consistency of stored information, which is indispensable for safeguarding users’ sensitive data. Reliable software with robust data integrity mechanisms is essential for making informed and precise decisions based on authentic and trustworthy information. By mitigating the danger of inaccurate or misleading data, data integrity supports better decision-making and prevents potentially unfavorable outcomes for businesses and their users.
There are a myriad of techniques that companies can implement in order to safeguard data integrity, among which code signing certificates emerge as a potent solution. For this, hashing algorithms are used. A hash function converts the data into a fixed-length digest (hash), which is subsequently used to affirm data integrity.
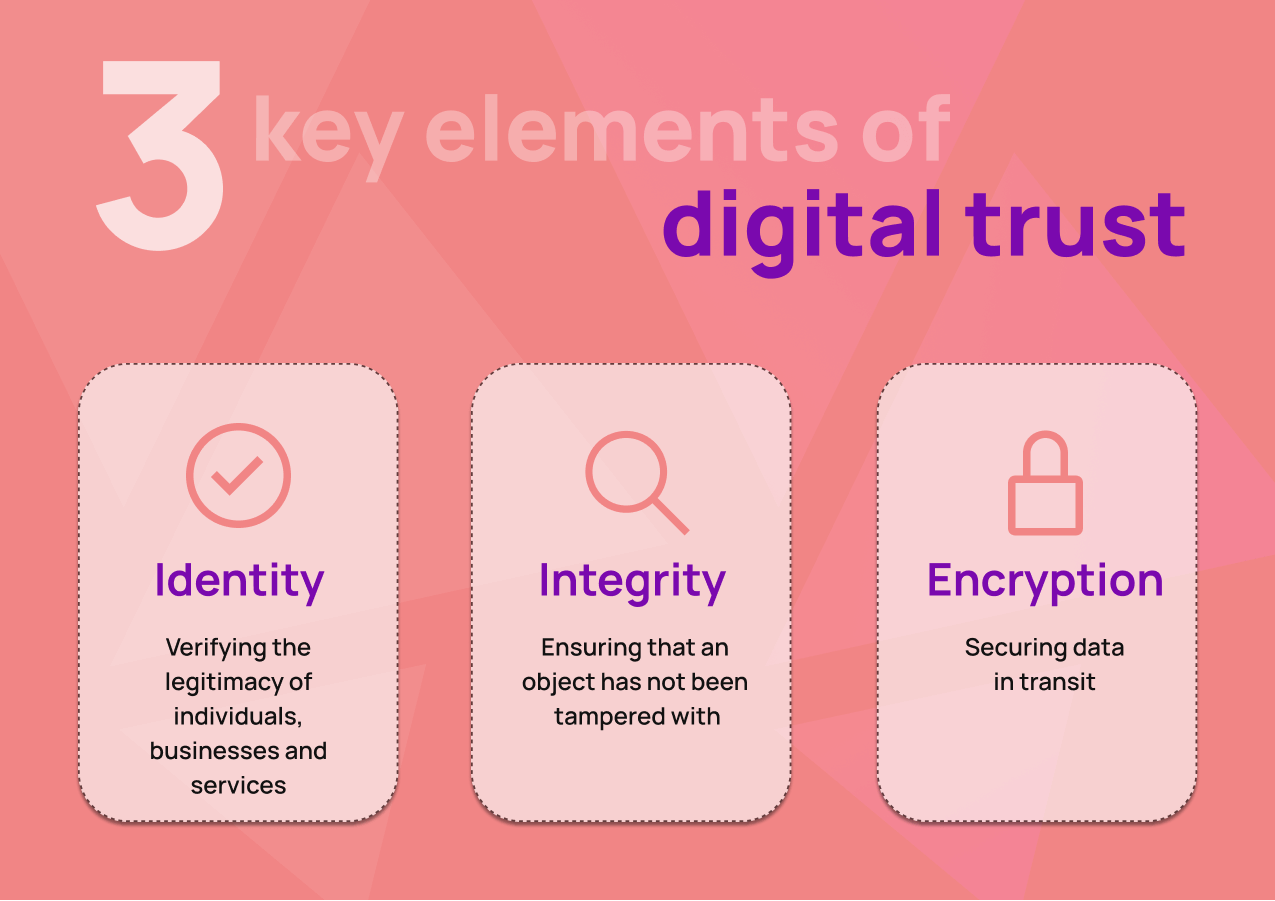
In order to establish a robust foundation for digital trust, organizations must embrace these three fundamental elements: encryption, identity management and data integrity. By doing so, they can not only foster secure and seamless interactions with stakeholders, but also safeguard their valuable data, intellectual properties and organizational reputation.
| Digital trust & encryption products | Purpose | Key features | Benefits |
| SSL/TLS certificates | Provide secure, encrypted communications between a website and an internet browser | Domain validation, organization validation, extended validation | Safeguards sensitive information, authenticates the identity of the domain, establishes trust |
| Code signing certificates | Protect software code and content by providing a layer of assurance that the content is unaltered and from a secure, verified source | Time-stamping, Microsoft Authenticode, Java app signing | Ensures trust in software or applications, protects against malicious tampering |
| Document signing certificates | Enables the signing of documents with a digital signature to authenticate the identity of the author and ensure the document has not been tampered with since signing | PDF signing, Microsoft Office and other format document signing | Secures digital document exchange, provides integrity and authenticity of documents |
| S/MIME certificates | Secure email communication by enabling encryption and digital signatures | Email signing, email encryption | Validates sender’s identity, ensures confidentiality and integrity of the email content |
The all-in-one checklist for establishing digital trust in business
Encryption
- Implement end-to-end encryption for sensitive data transmission
- Use the latest strong encryption algorithms (e.g., AES-256)
- Encrypt stored data (e.g., files, databases)
- Implement proper key management practices (e.g., key rotation, secure storage)
- Ensure that third-party tools and services use encryption best practices
- Regularly review and update encryption policies and standards
- Train employees on the importance of encryption and how to handle sensitive data
Identity
- Use a centralized identity and access management (IAM) system
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) for access to sensitive systems
- Use strong and unique passwords for all user accounts
- Regularly review and update user privileges and access controls
- Implement single sign-on (SSO) and password managers for secure and simple authentication
- Deploy security awareness campaigns to educate employees on the importance of strong passwords, MFA and avoiding phishing attacks
- Conduct regular audits of user accounts and access logs to detect unauthorized access or malicious activities
Integrity
- Employ secure coding practices and regularly review code for vulnerabilities
- Create, manage and enforce strict security policies and standards for employees, contractors and third-party vendors
- Regularly update software and systems to protect against known vulnerabilities
- Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS) and intrusion prevention systems (IPS) to monitor and prevent unauthorized access
- Use security information and event management (SIEM) systems for real-time monitoring and analysis of security events
- Deploy a comprehensive backup and recovery plan to ensure data integrity and availability
- Train employees on the importance of data integrity and how to avoid common threats (e.g., social engineering, phishing, malicious links)
The future of digital trust: a new era of authentication and security
As we advance into a future driven by digitization, our reliance on online ecosystems is increasing dramatically. Cases in point being e-commerce, digital banking, telehealth and remote work. This proliferation of digital touchpoints demands a robust framework of digital trust to secure sensitive information and uphold consumer confidence. Evolving consumer expectations for seamless, secure online experiences influence the competitive landscape and make digital trust absolutely essential, as opposed to simply a “nice to have” afterthought. As we venture forward, digital trust will remain vital for the expansive digital landscape, shaping business strategies and consumer choices.
From implementing PKI to adopting trust-based security solutions such as TLS/SSL certificates, code signing certificates, and document signing certificates, businesses have robust and effective strategies at their disposal. They should look to safeguard their digital environment and foster trust among users. Ensuring the safe conduct of digital business, InterNetX stands as a reliable partner, offering rock-solid encryption products from leading certificate authorities (CAs) like DigiCert that align with best practices and user expectations.